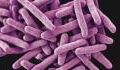
UK health officials have assured that the risk of the public contracting tuberculosis remains low, even as they work to control a spread of the disease. This assurance is coming in the wake of the death of a student at the University of Wales, Trinity Saint David after testing positive for TB.
Discover our latest podcast
No cause for alarm
According to express.co.uk, a team of experts has been working with the school to track down three people who were in contact with the deceased. Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from an infected person when they cough or sneeze.
Although not highly contagious, tuberculosis can be deadly, with the World Health Organization reporting that there’s been an increase in the number of deaths globally due to Covid-19. Director General of the WHO, Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said:
This report confirms our fears that the disruption of essential health services due to the pandemic could start to unravel years of progress against tuberculosis.

Symptoms and precautions
The disease mainly affects the lungs, with the potential to spread to other parts of the body such as the abdomen, bones and nervous system, the NHS says on its website. Although potentially serious, TB can be cured when detected early. Some common signs to look out for include:
- Cough that lasts more than 3 weeks. It usually produces phlegm which may be bloody
- Weight loss is another common symptom of TB as it causes one to lose appetite
- Most people who test positive for the disease also experience high temperature, while breaking into night sweats
According to WebMD, other symptoms include, feeling tired all the time, loss of appetite and chest pains. Dr Brendan Mason, consultant in communicable disease control for Public Health Wales, says people should know the signs of the disease for early detection and treatment.
If you have symptoms, we advise that you speak to your GP, who can provide you with the appropriate advice and refer you for TB screening if required.
Read more:
⋙ Tuberculosis and COVID: What are the common symptoms and differences?
⋙ Tuberculosis: This disease from the past could be making a comeback due to COVID
⋙ Pink eye, colds and cough among medical conditions that will no longer require prescriptions