Chickenpox In Children
Discover our latest podcast
1. What is chickenpox: Chickenpox is caused by the herpes zoster virus. Chickenpox is one of the most common childhood diseases. This is because it is very contagious - the virus is transmitted very quickly by air, when released into the atmosphere via a sneeze, for example. As a result, it is often enough for only one baby to become infected so that the whole nursery is affected.
The good news is that chickenpox in children is usually benign and once the child has had it they are immune to the virus for the rest of their life. In practice, nearly 90% of children contract it, most often between 1 and 8 years old.
Note: It is extremely rare to get chickenpox during pregnancy (9 out of 10 women are already immunized when they become pregnant), but this can have serious repercussions on the fetus (example: malformations). When in doubt, consult your doctor.
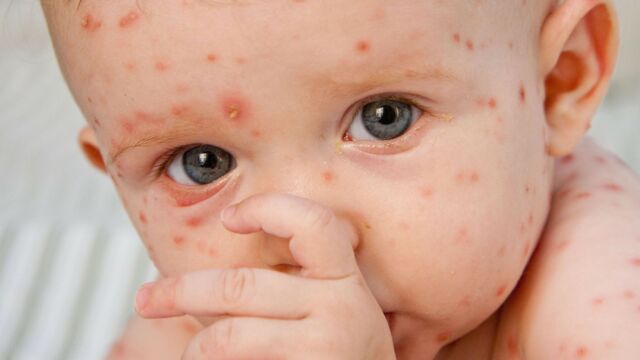
2. Symptoms of chickenpox: Chickenpox occurs about 15 days after infection. In general, baby will have a fever and seem tired. Nasal discharge may also be observed. But the most characteristic symptom of baby chickenpox is the rash.
It all starts with red spots appearing, usually on the back, stomach or face. The rash can spread quite quickly to the whole body. As the days go by, the pimples fill up with liquid and eventually form crusts. Generally, chickenpox spots are very itchy.
3. Chickenpox treatment: It is advisable to consult a pediatrician, if only to make sure that your baby is suffering from chicken pox and not from another illness. In addition, whilst baby chickenpox is mostly benign, it presents a risk of complications in babies of less than 6 months. Consult without delay as a precaution so that baby can receive preventative treatment.
Apart from this particular case, it is often enough to relieve the baby's symptoms while chickenpox is healing, especially with children's paracetamol for fever. It is also necessary to ensure that baby drinks enough and prevent them from scratching (risk of small scars or bacterial superinfection, treatable with antibiotics if necessary). Antihistamines are sometimes prescribed to calm the itching. You can also wash baby twice a day with warm water to relieve them. And put them in mittens!
Finally, keep baby home as they will remain contagious for ten days, as long as they have spots.